Elastic potential energy
Elastic potential energy can be stored in compressed or expanded springs or other elastic objects.
A spring has a tendency to return to its equilibrium position.
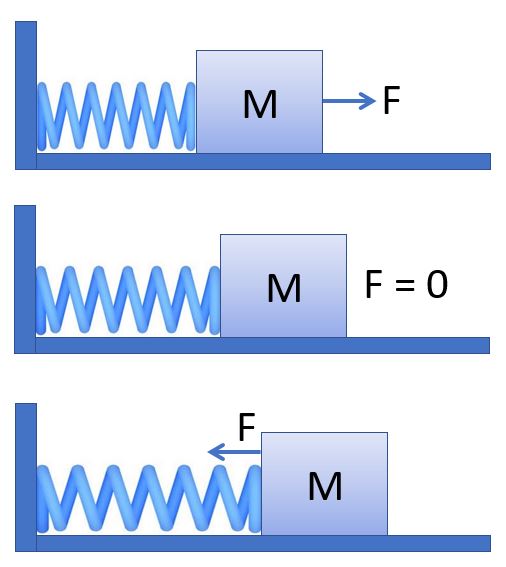
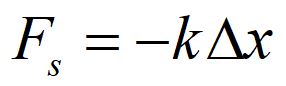
The force from a spring is proportional to the distance the spring is stretched or expanded from its equilibrium length. The minus sign indicates the force is in the opposite direction of the change in x. The constant k is a measure of the stiffness of the spring. This force relationship is known as Hooke's law.
This interactive PhET simulation illustrates the force for a compressed or extended spring.
This interactive PhET simulation illustrates properties of springs of various stiffness and internal friction.
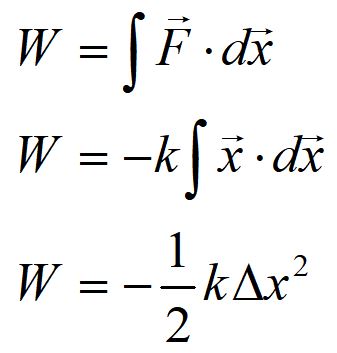
The area under a force curve as a function of x gives us the work done by a spring.
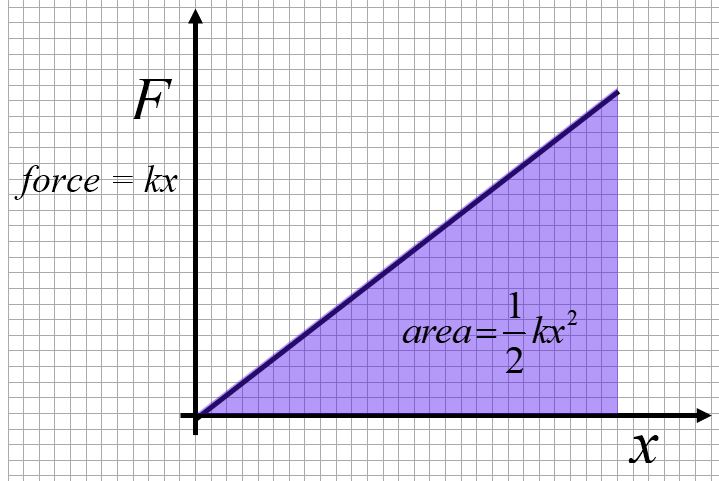
For example, consider the work done on a spring, F = kΔx. The area under the force curve is half of the rectangle with sides kΔx and Δx.
Practice problems
1. A 12 cm long spring is suspended from a beam. When a 1.6 kg steel ball is attached to the spring, the length of the spring increases to 18 cm.
A. How far will the string stretch if a 1.2 kg steel ball is attached instead?
B. How much work is done by the spring on the 1.2 kg steel ball?
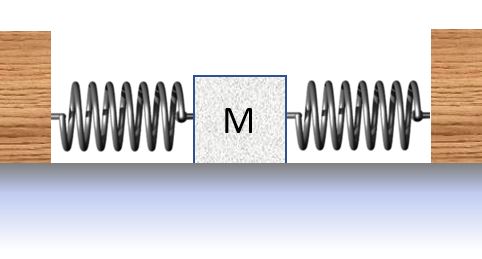
2. Two identical ideal springs are attached at their equilibrium lengths to a 1.4 kg block on a frictionless table as shown. The block is displaced 4.0 cm to the left by a 2.2 N force and held at rest. What is the spring constant of the springs?
Power
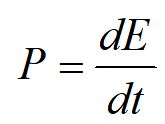
We define power as the rate of change of the energy of a system with respect to time. The standard unit for power is Watts, equivalent to joules/second.
The rate of energy transfer does not depend on what kind of energy is transferred. For the case where work is the source of the energy transfer, we can derive another expression for power:
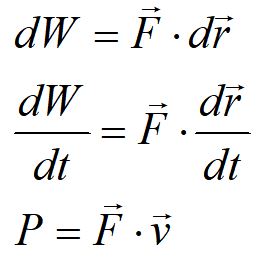
Here, we have expressed power as the dot product of force and velocity, for the case where force does not vary with time.
Practice problem
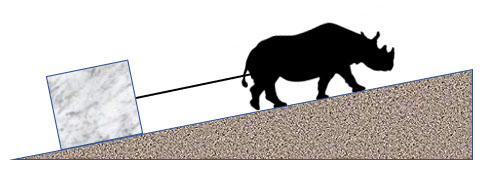
1. A rhinoceros drags a 150 kg marble block up a 14° incline at a steady pace of 3.2 m/s. The coefficient of friction between the ramp and the block is 0.28. What is the power output of the rhino is used to pull the block up the ramp?